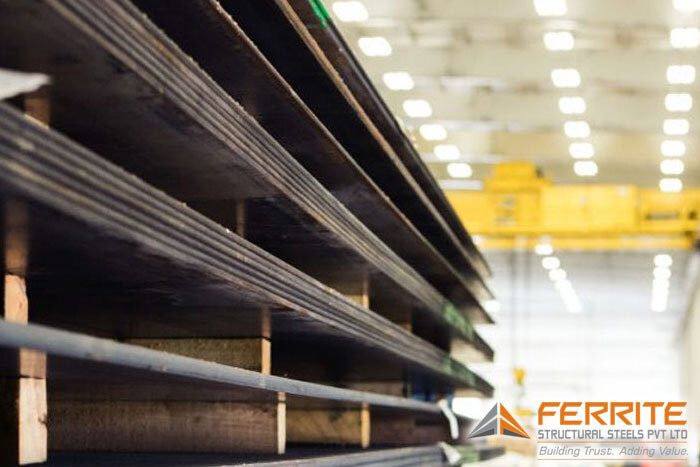
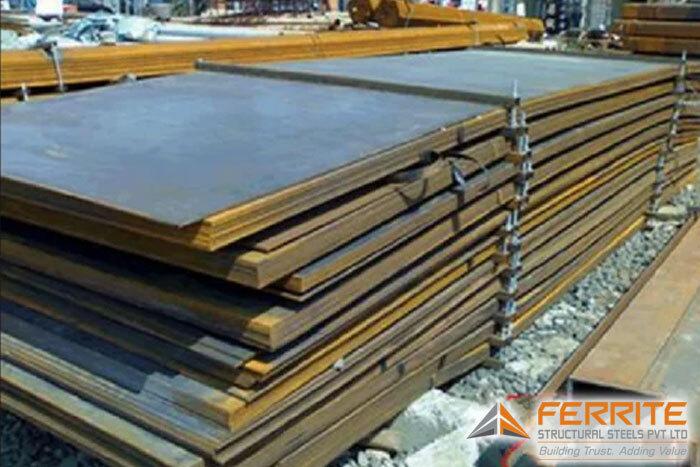
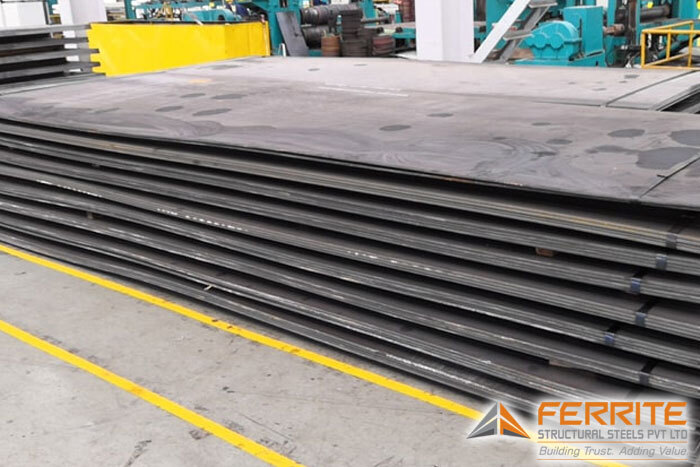
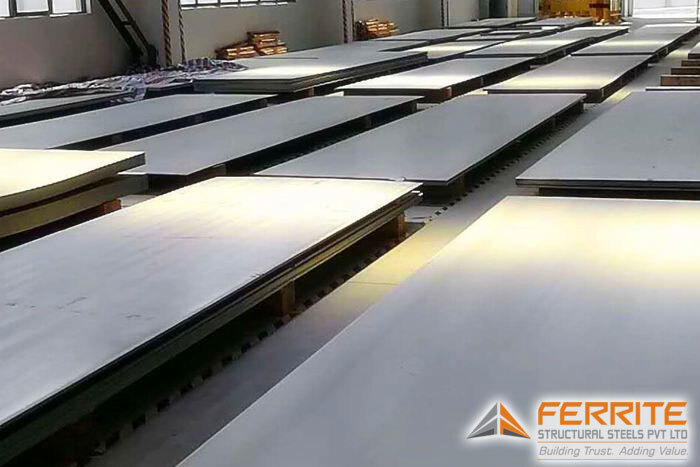
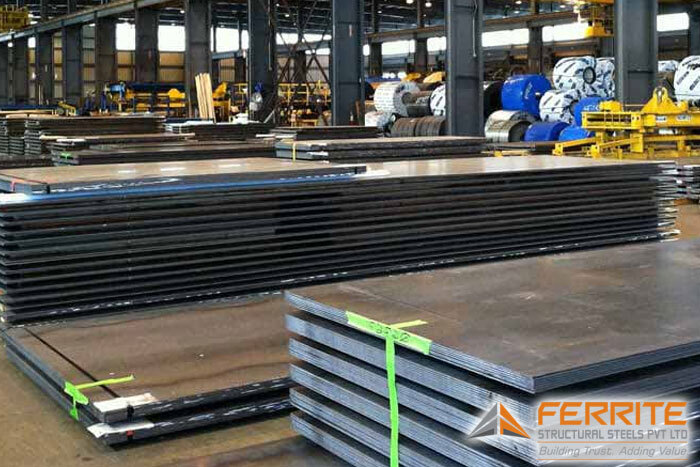
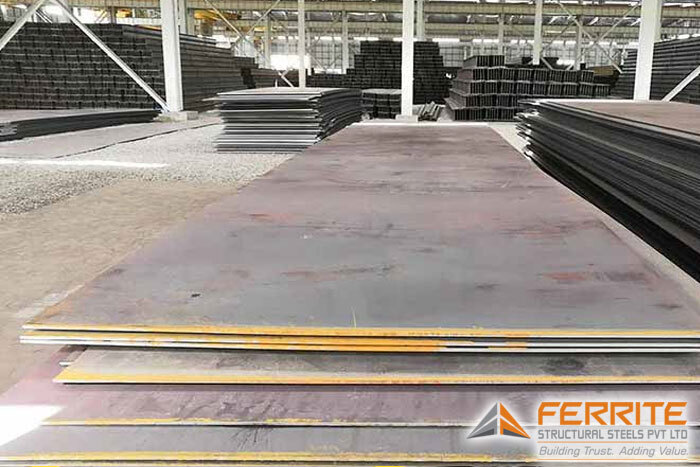
Pressure Vessel Steel Plate
Product Details:
- Recyclable non-recyclable
- Diameter customized lengths
- Product Name Steel Products
- Steel Type Stainless Steel
- Steel Product Type Steel Sheets
- Thickness Customize
- Shape Customized
- Click to View more
Pressure Vessel Steel Plate Price And Quantity
- 89000 INR/Gram
- 1 Ton Kilograms
Pressure Vessel Steel Plate Product Specifications
- Painted, galvanized, or standard mill finish
- Customized
- Other
- Customize
- Construction
- Steel Sheets
- Stainless Steel
- non-recyclable
- Steel Products
- as per requirement
- customized lengths
- Steel , Silver
Pressure Vessel Steel Plate Trade Information
- Cash Advance (CA) Cash in Advance (CID) Cheque
- 1 Kilograms Per Week
- 7 Days
- Standard, As per requirement,
- All India
- We are certified under the ISO 9001:2015 standard, with authorized distributor of Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) customer of the Steel Authority of India Ltd. (SAIL).
Product Description
Pressure vessel steel plates are specialized materials engineered to withstand high pressures and temperatures, ensuring the safe containment of gases and liquids in various industrial applications. Their exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to stress make them indispensable in the fabrication of boilers, storage tanks, and heat exchangers.‹
Key Features:
High Tensile Strength: These plates are designed to endure significant internal pressures without compromising structural integrity.
Notch Toughness: They exhibit resilience against cracking, even when subjected to sudden impacts or fluctuating pressure conditions.
Ductility: The material's ability to deform without fracturing allows for the absorption of energy, enhancing safety under stress.
Fatigue Resistance: Engineered to resist wear from repeated pressure cycles, these plates ensure longevity in demanding environments.
Grades and Specifications:
Several standards govern the production of pressure vessel steel plates, each tailored to specific applications:
ASTM A516: Ideal for moderate to low-temperature service, this grade offers excellent weldability and notch toughness, making it suitable for various pressure vessels and boilers.
ASTM A285: Suited for fusion-welded pressure vessels, particularly those operating at low pressures, due to its lower tensile strength.
ASTM A537: This heat-treated carbon steel plate is used in pressure vessel applications requiring high tensile and yield strength, as well as resistance to high-pressure and temperature conditions.
ASTM A387: A chromium-molybdenum alloy steel plate designed for elevated temperature service, commonly used in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+















 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free
